The electric field at an axial point of an electric dipole:
As shown in figure an electric dipole consisting of charge +q and -q , separated by distance 2a and placed in a vacuum . Let P be a point on the axial line at distance r from the center O of the dipole on the side of the charge +q.
 |
| The electric field at an axial point of a dipole |
By this picture, you can see the resultant electric field at an axial point of a dipole this value is 3.51 V/m but if you start increasing distance mean point p on the axial point of dipole than field start decreasing.
 |
| The electric field at an axial point of a dipole at a distance |
so here you can see that if I increase the distance P on the axial point of a dipole than the electric field start decreasing and its value will be 1.72 V/m. so what I found? , with increasing the distance the electric field will start decreasing.
 |
| The electric field at an axial point of a dipole at a far distance |
Calculation of the net electric field at an axial point of a dipole:
1. Electric field due to charge -q at point P is
2. Electric field due to charge +q at point P is
Note- Where
Hence the resultant electric field at point P is
or
Here P= q x 2a = dip[ole moment .
for r>>a , a2 can be neglected compared to r2
Note- The electric field at any point of the dipole acts along the dipole axis from negative to the positive charge i.e in the direction of dipole moment 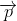 .
.
